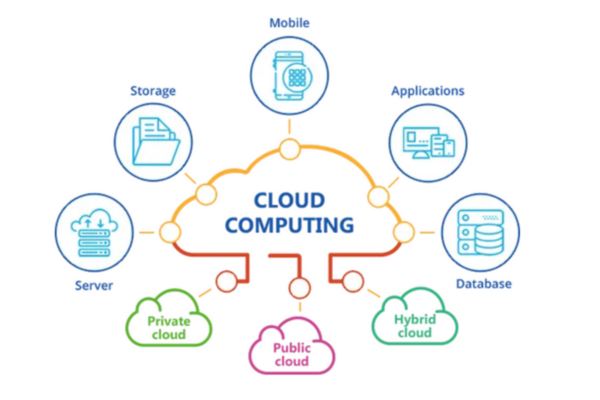
Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access and store data and applications on remote servers, rather than on a local computer or physical server. This technology provides a range of computing resources over the internet, including storage, processing power, and software applications, all delivered on demand.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern IT solutions, revolutionizing how businesses and individuals manage data and applications. Offering unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and efficiency, cloud computing enables users to access vast computing resources over the internet, transforming traditional IT infrastructure.
Table of Contents
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
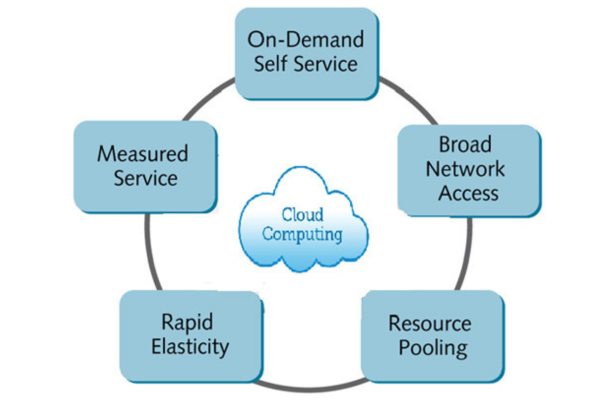
- On-Demand Self-Service:
- Users can automatically provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
- Broad Network Access:
- Services are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by various client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations).
- Resource Pooling:
- The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand.
- Rapid Elasticity:
- Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released, in some cases automatically, to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand. To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be appropriated in any quantity at any time.
- Measured Service:
- Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for the provider and consumer of the utilized service.
Types of Cloud Computing Services:
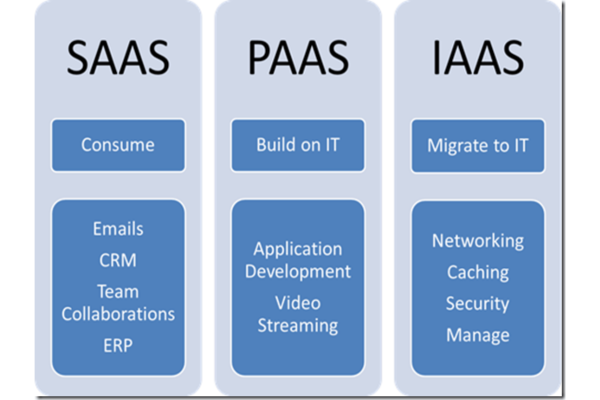
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- Offers hardware and software tools over the internet, typically those needed for application development. Examples include Google App Engine and Microsoft Azure PaaS.
- Software as a Service (SaaS):
- Delivers software applications over the internet, on a subscription basis. Examples include Google Workspace, Microsoft Office 365, and Salesforce.
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
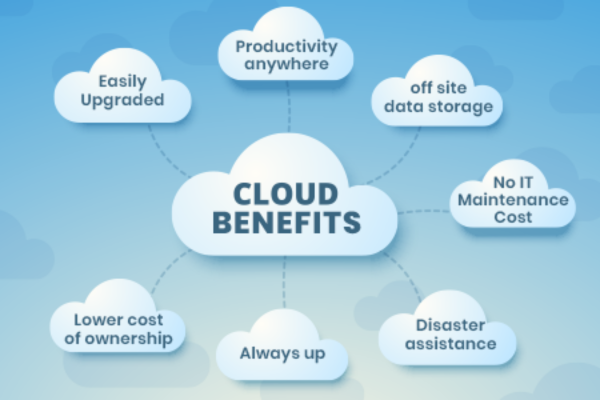
- Cost Efficiency:
- Reduces the capital expense of buying hardware and software and setting up and running on-site data centers.
- Scalability:
- Easily scale up or down your IT resources as needed with cloud computing services.
- Performance:
- Major cloud services run on a worldwide network of secure data centers, which are upgraded to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing hardware.
- Speed and Agility:
- Vast amounts of computing resources can be provisioned in minutes, typically with just a few mouse clicks, giving businesses a lot of flexibility and taking the pressure off capacity planning.
- Security:
- Many cloud providers offer a set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen your security posture overall, helping protect data, apps, and infrastructure from potential threats.
Use Cases of Cloud Computing:
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery:
- Cloud solutions can be used for data backup and disaster recovery, offering a reliable way to ensure data safety and availability.
- Software Development and Testing:
- Cloud platforms provide environments for developers to build, test, and deploy applications efficiently.
- Big Data Analytics:
- Cloud computing can process vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently, making it ideal for big data analytics.
- Hosting Websites and Blogs:
- Websites and blogs can be hosted on cloud servers, providing high availability and performance.
- Content Streaming:
- Platforms like Netflix and Spotify use cloud computing to stream content to users.
Conclusion:
In essence, cloud computing provides a flexible, scalable, and efficient way to manage computing resources, driving innovation and operational efficiency across various industries.